Ergonomics
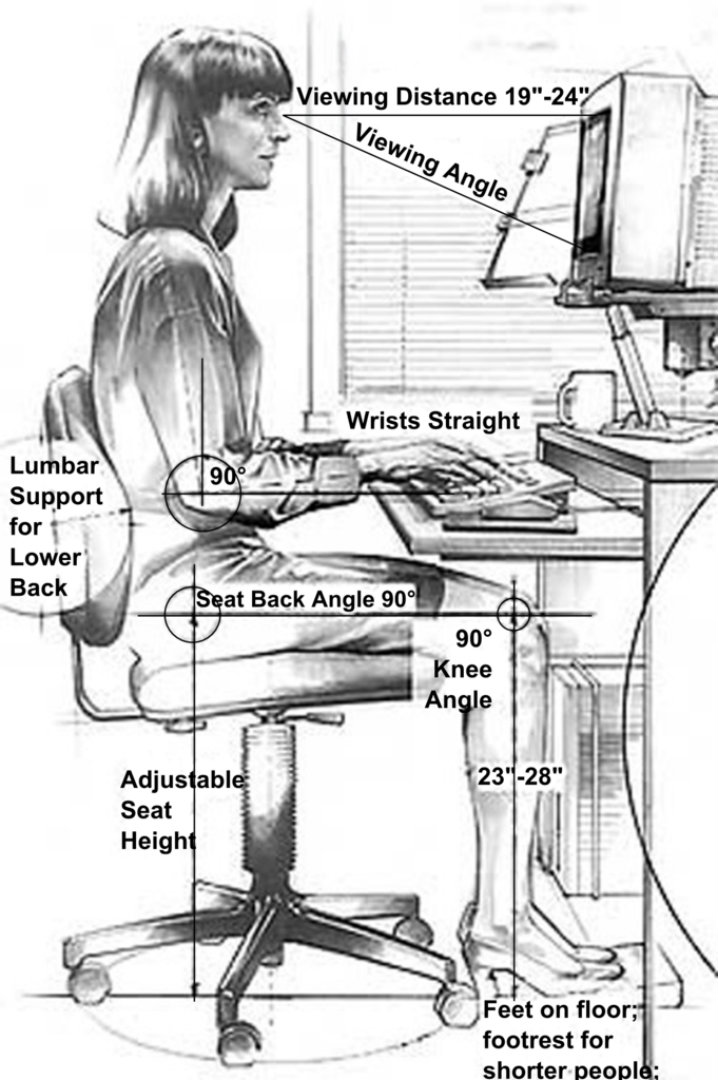
Ergonomics is the science of designing the job, equipment, and workplace to fit the worker. Proper ergonomic design is necessary to prevent repetitive strain injuries, which can develop over time and can lead to long-term disability.
Members of the TWU community that have concerns about the ergonomics of their workstation, or any work tasks they perform, are encouraged to contact EH&S for an ergonomic assessment. If you are experiencing musculoskeletal discomfort or health issues that might be related to your workspace, or to ensure your workspace is ergonomically set up regardless of any issues, please fill out the Ergonomic Questionnaire. Students should fill out the Student Ergonomic Questionnaire.
See a short video about office ergonomics from the State Office of Risk Management, which is both humorous and informative.
Definitions
- Musculoskeletal Disorder (MSD): an injury or illness of soft tissues of the upper extremity (fingers through the upper arm), shoulders and neck, low back, and lower extremity (hips through toes). It is primarily caused or made worse by workplace risk factors, such as sustained and repeated exertions or awkward postures and manipulations. Included are disorders of the muscles, nerves, tendons, ligaments, joints, cartilage, and spinal disks. Medical conditions generally develop gradually over a period of time and do not typically result from a single event. Injuries arising from slips, trips, falls and similar accidents are not considered to be an MSD. Typical injuries include lower back pain, neck pain, arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, tendinitis, and golfers'/ tennis elbow.
- Ergonomics: Addresses the fit between the person, task, and the environment to help prevent musculoskeletal disorders (i.e., low/upper back, shoulder, wrist area) and optimize productivity and promote safety and health.
- Biomechanics: a field of study that uses the laws of physics and engineering concepts to describe the motions of body parts and the forces acting upon them during normal daily activities
- Neutral posture: a comfortable working posture that reduces the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. The joints are naturally aligned with elbows at the side of the body and wrists straight. The more the joint deviates from a neutral posture, the greater the risk of injury.
- Awkward posture: deviation from the ideal working posture. For example, students may be slouched or bent forward when studying.
Page last updated 1:42 PM, November 10, 2022